In emergency medicine, quick and accurate assessments can make the difference between life and death. One such vital component of immediate evaluation is pupil reactivity. Often referred to as the “window to the brain,” the eyes provide critical insights into a patient’s neurological status. Through pupil reactivity, medical professionals can gather essential data about brain function and potential underlying conditions.
This blog explores why pupil reactivity is a crucial indicator in emergency settings and how advanced neurological tools enhance the precision of pupil assessments.
Pupil Reactivity in Emergency Medicine
Pupil reactivity refers to the eye’s ability to constrict and dilate in response to light. The pupils’ speed, size, and symmetry offer a wealth of information regarding the patient’s central nervous system (CNS) function. Pupil evaluation is often the first step in a neuro exam because of its simplicity and non-invasive nature. Yet, despite its simplicity, pupil reactivity is incredibly telling.
In emergencies, pupil size and reaction time changes could signal increased intracranial pressure (ICP), brain injury, or neurological impairment. Immediate attention to pupil changes can provide a clear indication of the severity of the condition and direct healthcare professionals toward appropriate interventions.
The Role of Pupil Assessment in Neuro Exams
A neuro exam is a comprehensive evaluation of the nervous system. Within this examination, pupil assessment plays a critical role. Historically, clinicians have used penlights to manually check for changes in pupil reactivity—a task that requires subjective interpretation. However, manual pupil evaluation can be prone to errors, especially in stressful emergency settings where every second counts.
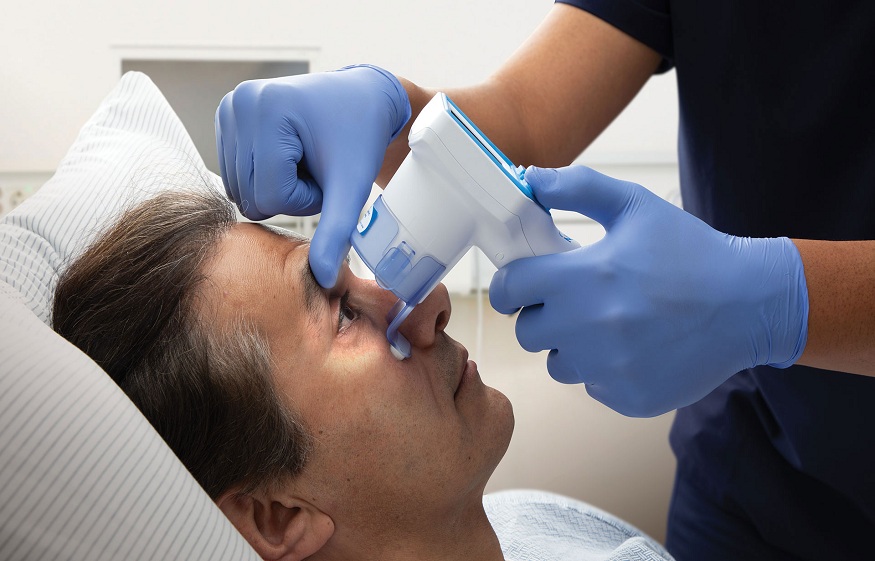
Today, advanced neurological tools like automated pupillometers have made pupil assessments more precise and reliable. These devices can detect subtle changes in the size and reaction of the pupils, which may not be apparent through traditional methods. Healthcare providers can make faster, more informed decisions during critical situations by providing accurate data on pupil reactivity.
Why Pupil Reactivity is a Key Indicator of Brain Health
The connection between the eyes and brain is intricate and direct. When brain function is compromised, one of the first systems to be affected is pupil reactivity. Monitoring pupil changes allows physicians to assess brain health in real-time, particularly in patients with head injuries, stroke, or brain hemorrhages.
Key conditions in which pupil evaluation becomes essential include:
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): In cases of trauma, changes in pupil size may indicate brain swelling or bleeding.
Stroke: Abnormalities in pupil reactivity can indicate ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, guiding the urgency of treatment.
Intracranial Pressure (ICP): Elevated ICP can compress cranial nerves, affecting the pupils’ ability to react normally to light.
The Neurological Pupil Index (NPi): Advancing Pupil Evaluation
Recent advancements in neurological tools have led to the creation of the Neurological Pupil Index (NPi). This index provides a quantifiable measure of pupil reactivity, removing much of the subjectivity inherent in manual assessments. The NPi system analyzes a variety of parameters, such as the size, shape, and reactivity of pupils, and assigns a numerical value to reflect the health of the patient’s brain function.
The NPi can be particularly useful in emergency medicine because of its objectivity. Rather than relying on a human’s interpretation of pupil behavior, the NPi provides a standard measure that can help medical teams track a patient’s neurological status over time. If the NPi value begins to decrease, it may signal that the patient’s condition is worsening, prompting timely intervention.
Real-World Applications of Pupil Assessment in Emergency Medicine
In the chaotic environment of the emergency room, time is often limited, and decisions must be made quickly. This is where advanced neurological tools like automated pupillometers and the NPi become invaluable.
For example, a patient arriving with head trauma may show no obvious external signs of distress, but a change in pupil reactivity could reveal a hidden brain injury. By using tools like the NPi, clinicians can detect and respond to these hidden signs long before more overt symptoms arise. Similarly, in cases of suspected stroke, rapid pupil evaluation can guide the decision to administer clot-busting drugs or perform surgery.
Conclusion
Pupil reactivity is much more than a simple reflex; it’s a vital sign that offers insight into brain function, making it an indispensable tool in emergency medicine. Through a combination of traditional neuro exams and advanced neurological tools like the NPi, medical professionals can quickly assess neurological health, ensuring swift and accurate treatment.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.